Bio diesel

Bio diesel
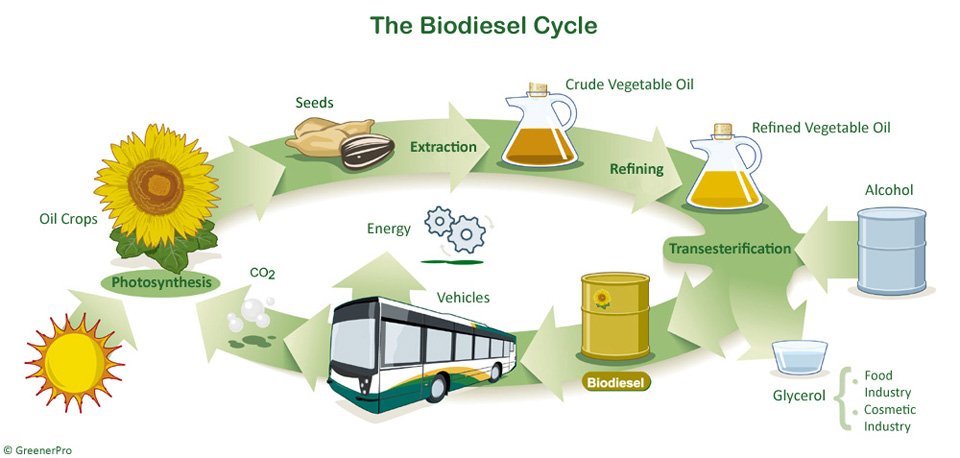
Bio diesel is a biodegradable, clean burning alternative fuel, produced from renewable resourses which can guarantee a green-house gas (GHG) saving of 90% and more compared to its fossil substitute.
The most used feedstocks for biodiesel production are:
- Vegetable oils,
Rapeseed oil, soyabean oil, sunflower oil, palm oil ecc.
- Raw materials & By –products,
Used Cooking Oils (UCO), free fatty acids (FFA), animal fats ecc.
Types of biodiesel:
- Rapeseed methyl ester (RME) is mainly produced in Europe;
- Soy methyl ester (SME) comes mainly from the Americas
- Palm methyl ester (PME) from Asia, in particular Malaysia and Indonesia.
- Fatty acid methyl ester (FAME)
- Used Cooking oil methyl ester (UCOME)
- Tallow methyl ester (TME)
Prices
Prices is depend of their different cold filter plugging points (cfpp) and of % of GHG savings.
RME will usually be proposed with a guarantee of -14°C cfpp, SME with -4°C and PME
15°C. These numbers represent the cfpp point of the product on its own rather than the
overall cfpp point once blended into fossil fuel. The exact cfpp point may vary according to quality.
Fatty acid methyl ester (FAME)
Fatty acid methyl ester (FAME) refers to European blends of biodiesel. These blends contain different quantities of the pure vegetable and/or tallow oil methyl esters and/or recycled used cooking oil depending on the cfpp point desired.
Prices for the three most used FAME cfpp levels are: 0, -5 and -10. All FAME quotes are for unadditivated material.

Benefits for using Biodiesel
- Biodiesel contains no fossil fuel
- It can be blended at any level with petroleum diesel to create a biodiesel blend.
- Biodiesel is simple to use, biodegradable, non-toxic, and, if pure and unadditivated, essentially free of sulphur and aromatics
- Is safe to transport and is not considered a hazardous material
- It is more lubricating than diesel fuel, it increases the engine life and can be used in place of sulfur
- It powers any conventional, unmodified diesel engine
- Greenhouse gas emissions are reduced (including CO2), as well as carbon monoxide (CO) emissions and emissions of particles and other polluting products.
- Biodiesel can be used as a pure fuel or blended with petroleum in any percentage. In Italy is blended at a rate of 7% biodiesel more or less into almost all diesel sold.
- It can also be used in most modern diesel engines without modification, including those in passenger cars, sport utility vehicles, light trucks, buses, ships, trains, off-road heavy equipment and mining equipment, as well as for home heating fuel, power generation and in two-stroke engines (as a mixing agent).
Biodiesel is made through a chemical process called transesterification whereby the glycerine is separated from the fat or vegetable oil. The process leaves behind two products:
- methyl esters (the chemical name for biodiesel)
- glycerine (a by-product usually sold to be used in soaps and other products)
100% biodiesel must meet EU quality standard EN 14214
The recast directive 2018/2001/EU
The energy sector is responsible for more than 75% of the EU’s greenhouse gas emissions. Increasing the share of renewable energy across the different sectors of the economy is therefore a key building block to achieving an integrated energy system that delivers on Europe’s ambition of climate neutrality.
In Europe, the Renewable Energy Directive (RED) stipulates that renewable energy
should have a minimum 20% share in transport by 2020 and that this energy should come
from sustainable feedstocks. This has resulted in a greater amount of RED certified
biodiesel becoming available in the market. Now RED sets rules for the EU to achieve its 32% renewables target by 2030.
The double counting market in EU
The Renewable Energy Directive (RED 2009/28/CE) states that waste-based biofuels can be counted twice in the calculation of the shares of renewable energies in transport.
The double counting system encourages the use of second-generation waste-based biofuels produced from such feedstocks as Used Cooking Oil or Animal Fat CAT 1 and 2 (not intended for consumption). As these raw materials represent a great savings potential regarding GHG emissions and considerable environmental advantages forthe production of biofuels, most of the EU member states have decided to establish the inciting double counting system.
In terms of storage, handling and distribution, biodiesel is as safe as diesel, and it has a much higher ignition point. Biodiesel can be safely stored without degrading for up to six months to keep for longer than that stabilising additives are needed.
The biodiesel and renewable diesel industry is on the “RISE”. The National Biodiesel Board hosted more than 550 biodiesel and renewable diesel producers, distributors, retailers, and other industry advocates virtually to share the direction of the industry now and in the future.
Throughout the conference, industry leaders shared how they intend to keep momentum rising in the next decade to meet NBB’s Vision of six billion gallons by 2030.
Legend:
*Feedstock- is a material that is used to produce something in an industrial process
*Biodegradable- refers to the ability of things to get disintegrated (decomposed) by the action of micro-organisms such as bacteria or fungi biological (with or without oxygen) while getting assimilated into the natural environment. There’s no ecological harm during the process.
